취업전 교육을 받을 때도, 취업 후 혼자 사이드 프로젝트를 진행할 때도 DB 접근 기술로 JPA를 선택했고 @OneToMany 같은 어노테이션을 이용해서 DB 구성을 했는데 이 때 사용가능한 옵션 중 하나인 fetch와 EAGER, LAZY 로딩에 대한 궁금증이 생겼다. 이론적인 부분은 알고있다는 가정하에 확인하는 코드들만 설명할 것 이기에 이론은 잘 정리된 다른 블로그를 참고하시리 바랍니다.
GitHub - N1ghtsky0/playground
Contribute to N1ghtsky0/playground development by creating an account on GitHub.
github.com
프로젝트 구성
- 메인 엔티티와 1대다 속성을 가지는 서브엔티티 2개를 구성 (각각 EAGER, LAZY) 적용
- RestAPI로 테스트를 진행하며 찍히는 콘솔 로그를 통해 메인 엔티티와 관련된 쿼리가 실행되는 순간이 어떤 순간들인지 확인
build.gradle
dependencies {
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter'
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-data-jpa'
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web'
compileOnly 'org.projectlombok:lombok'
runtimeOnly 'com.h2database:h2'
annotationProcessor 'org.projectlombok:lombok'
testImplementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-test'
testImplementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-test'
}
application.yml
spring:
datasource:
driver-class-name: org.h2.Driver
url: jdbc:h2:mem:test
username: root
password: 1234
h2:
console:
enabled: true
jpa:
hibernate:
ddl-auto: create
properties:
hibernate:
format_sql: true
show_sql: true엔티티 구성
// MainEntity
@Getter
@Builder
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@Entity
public class MainEntity {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long seq;
private String name;
}
// SubEntity
@Getter
@Builder
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@Entity
public class SubEagerEntity {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long seq;
private String name;
@ManyToOne(fetch = FetchType.EAGER) // SubLazyEntity 에서는 FetchType.LAZY 적용
private MainEntity entity;
}API 명세
※ 컨트롤러 부분 소스코드는 github 참고 바랍니다.
| API명 | 엔드포인트 | http method | param | requestBody | 비고 |
| 메인 엔티티 저장 | /main | POST | {"name": string} | ||
| 메인 엔티티 전체 조회 | /main | GET | |||
| 메인 엔티티 개별 조회 | /main/{int} | GET | |||
| 서브 엔티티 저장 | /sub | POST | {"name": string, "seq": int, "flag": string} |
||
| 서브 엔티티 전체 조회 | /sub | GET | flag: string | flag값: {'e', 'l'} | |
| 서브 엔티티 개별 조회 | /sub/{int} | GET | flag: string | flag값: {'e', 'l'} | |
| 지연 로딩 시점 확인 | /sub/lazy/test/{int} | GET | flag: string | flag값: {'t', 'f'} |
결과
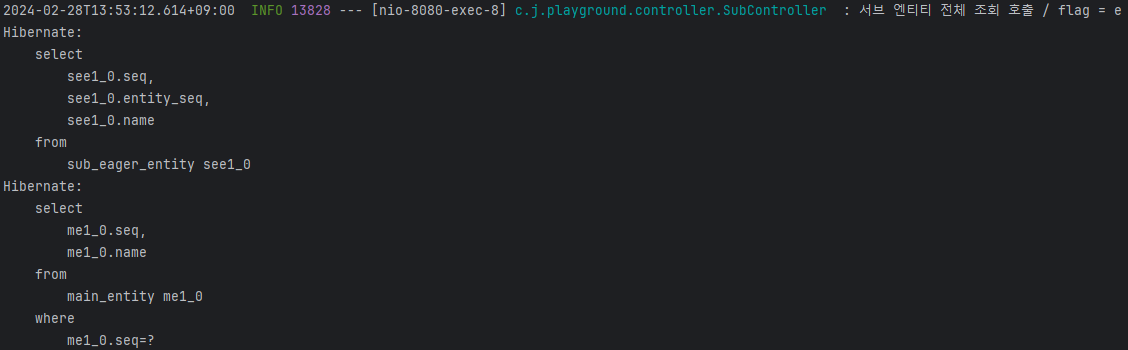

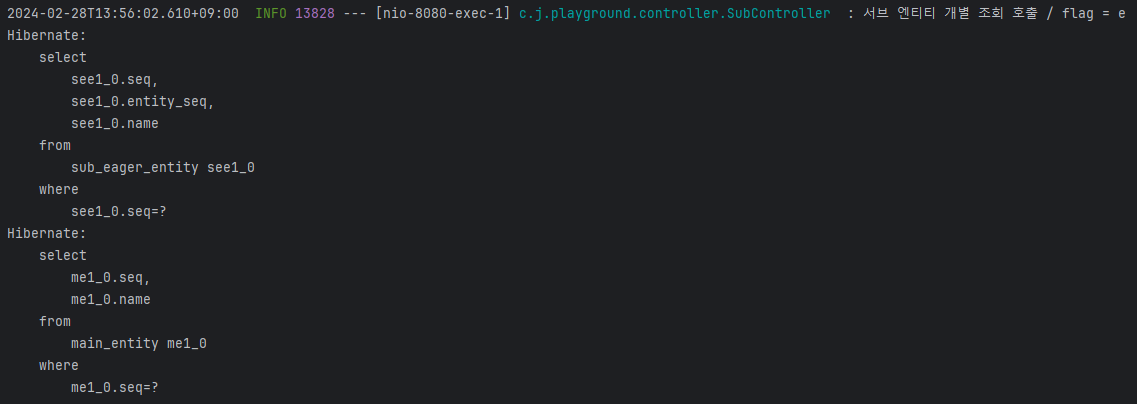
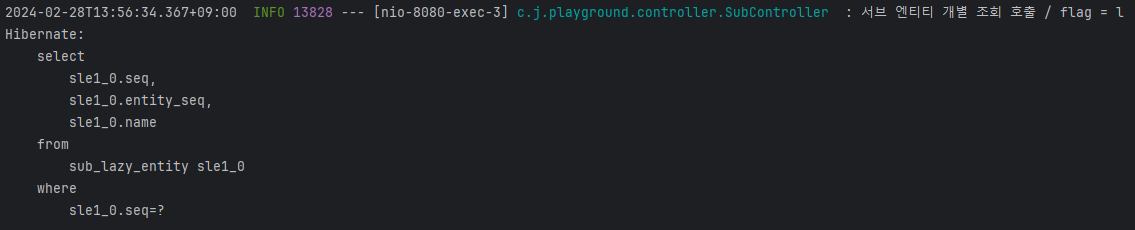
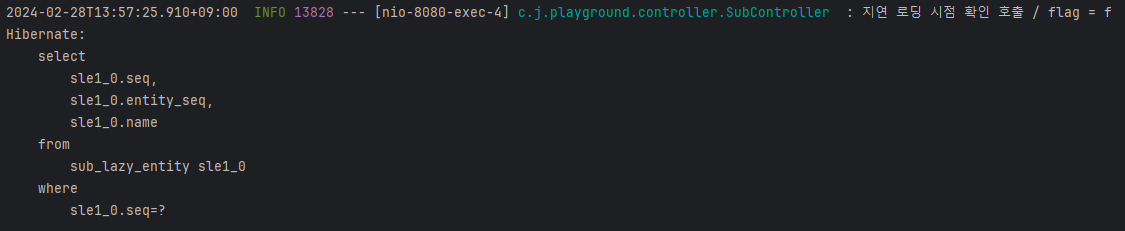
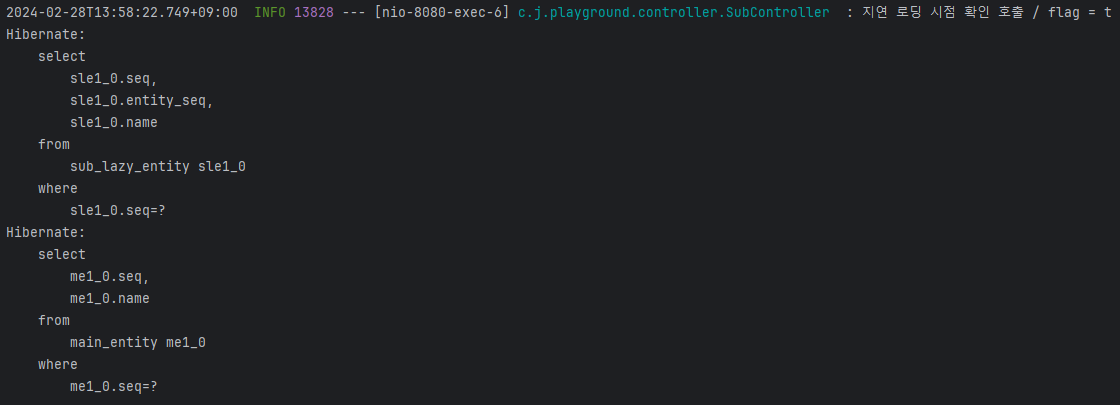
@OneToMany 와 같이 연관관계가 있는 엔티티를 조회할 때 발생하는 N+1 문제가 어떤 것이고 Lazy 로딩을 통해 해당 문제가 왜 해결된다고 하는 것인지 알 수 있었다.
'코딩 공부 > SpringBoot' 카테고리의 다른 글
| SpringBoot 3 + JWT(jjwt 0.12.5) + Spring security (0) | 2024.03.08 |
|---|---|
| 스프링부트 다중서버 세션관리 구현해보기(spring security + redis) (0) | 2024.03.04 |
| 스프링 부트 로컬 정적 리소스 사용하기 (WebMvcConfigurer) (0) | 2024.02.21 |
| spring devtools livereload 기능 사용하기 (intellij) (0) | 2024.02.19 |
| 스프링 시큐리티 - 회원가입, 로그인, 권한별 페이지 접근 설정 (0) | 2024.01.20 |